Electric Vehicles: A Ride to a Greener Future?

Vehicle emissions are one of the biggest contributors to air pollution. In Australia, transport is the third largest contributor of greenhouse gas emissions, with cars causing close to half of transport emissions.
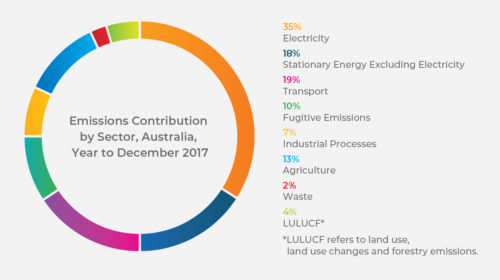
Since 1990, transport emissions have grown by nearly 60%, the most over any other sector. In fact, Australia is ranked the second worst in an international scorecard for transport energy-efficiency.
Thankfully, the automobile industry has developed solutions that can help reduce the emission of greenhouse gases. Studies have shown that through the development and use of electric vehicles (EVs), air quality has shown significant improvement. A 2019 study conducted by researchers at the Northwestern University shows that EVs have a net positive impact on air quality and climate change even when their electricity is sourced from combustion.
In effect, EV adoption reduces carbon emissions and becomes beneficial to the public’s health, according to the study’s senior author Daniel Horton.
What are EVs?
Electric vehicles are a type of alternative vehicle that run on one or more electric motors that are powered by batteries. One of the significant differences of EVs from conventional vehicles is that they can be charged by plugging them in to an off-board electric power source rather than being fueled by petroleum or diesel. However, there are also hybrid EVs which only partially run on electric motors and the remaining is powered by petrol.
All-electric vehicles (AEVs) run purely on electricity and have an average electric range of 135km, and up to 500km for a few luxury models. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) are powered by both electricity and fuel, which can be a more flexible option if an AEVs range isn’t enough.
The charging time for EVs ranges based on the model of the car as well as the type of charging port used. Publicly accessible ‘fast-charging’ outlets can recharge an EV battery in 30 minutes, while regular outlets called ‘Level 2 chargers’ can take up to a four hours. In 2016, RAC created Australia’s first Electric Highway, providing frequent charging stations, giving WA driver’s the ability to travel the state in the most sustainable way possible.
Some popular names in EV include brands like Tesla and Hyundai. Tesla is known for the Tesla Model S, which has established itself in the EV industry as a trendsetter for its luxurious style. Hyundai is also powering the market with its Ioniq Electric model that comes in an AEV and PHEV variant, and its newest EV model, the Kona Electric. Other well-known EV cars for everyday use include the Volkswagen e-Golf, the Nissan Leaf and the Kia Soul EV.
Environmental Impacts of EVs
EVs are widely known to help reduce the harmful emissions of greenhouse gases such as CO2. Electric vehicles don’t produce any gas exhaust emissions, so therefore are considered zero-carbon. Hybrid EVs produce significantly lower emissions compared to conventional cars even when it switches over to the combustion engine to run.
There is also a growing trend in using recycled materials and bio-based materials. The Nissan Leaf’s interior and bodywork are partly made from green materials such as recycled water bottles, plastic bags, reused car parts and secondhand household appliances.
What are the benefits of EVs for the consumer?
- Reduces fuel costs
With fuel prices constantly fluctuating, you’ll have peace of mind knowing running an EV costs less than half of what it costs to run a standard vehicle. In Australia, it costs about $4.50 in electricity for an EV to travel 100km. It would cost the average car about $16.65 to travel 100km.
- Energy efficiency
Because they rely solely on internal combustion engines, regular cars aren’t energy efficient. EVs on the other hand are more efficient by 60 to 77% because they use regenerative braking which recovers the energy wasted when regular cars use brakes.
- Less maintenance costs
Maintaining an electric car costs approximately one-third of the current costs of maintaining a fuel-powered car. You don’t have to worry about changing the oil or replacing fuel filters, and other routine replacements that they regularly need. While you will need to replace the battery in your EV, this is usually only every 8 years or so.
- Energy independence
EVs do not require fuel to work and thus can be powered by any resource that can generate electricity. If you have a solar PV system installed in your home, you can use the excess energy generated from the panels to power your car, reducing the need to rely on public stations and eliminating carbon emissions.
- Better for your health
One of the importance of adapting EVs for everyday use are the benefits it can give to public health. In 2018, nearly all the 1.3 billion vehicles worldwide were powered by internal combustion engines. This causes carbon emissions that are responsible for air pollution, thus raising public health concern. Using EVs improves air quality and their regenerative brakes produce less emissions than conventional fuel-powered vehicles, leading to better living conditions and overall improved health.
EVs for Economic Growth
Burning finite resources like oil to power our cars not only costs the environment, but the economy as well. In just one year (2017-2018), it cost Australia more than $33 billion in imports of petroleum. Our reliance on petroleum makes us vulnerable to supply disruptions and price hikes. However, once you have the infrastructure, renewable energy is free and abundant. The increasing demand for a dependable energy source encourages innovation and growth in the sources of renewable energy.
Infinite Energy offers Electric Vehicle Chargers designed for private, commercial and public use. If you’d like more information, please contact us today.


